Submitted by Raul Ilargi Meijer via The Automatic Earth blog,
China never had an actual economic model or growth model. It simply printed an obscene amount of money, especially after 2008, and used it to build factories, 30-story see-through apartment blocks and highways into nowhere cities, without giving much if any thought to where this would lead when their formerly rich western customers had less to spend on its ever increasing amount of ever more useless products, or when its workers would stop spending ever more on apartments as investments, or when no more roads and bridges were needed because nowhere was already in plain sight. Or all of the above. It was ‘to infinity and beyond’ from the start, but that’s a line from a kids’ fantasy story, not a 5-year plan or an economic model.
Going into its 10-day, 3,000 delegates National People’s Congress opening on Friday, China was facing -and very much still is- two major and interconnected problems. Both are problems that the country has never faced before -not a minor point to make. The first is a giant debt load, one that could easily be as high as $40 trillion, or 350% of GDP, once one includes the shadow banking system (watch the shadows!). The second is the Communist Party’s -economic- credibility.
The debt problem is impossible to solve without very far-reaching restructurings of both the debt itself and of the entire Chinese economy. There appears to be a problem within the problem, however: the Party neither looks prepared to truly tackle the debt nor does it seem to know how.
As for the credibility issue, the very fact that a 5-year plan will be unveiled is the perfect in-a-nutshell illustration of what’s ailing Beijing. Not only does it hark back to communist days of old, not exactly a confidence booster, but trying to look 5 years ahead in today’s global economy is in itself not credible. It forces the Party to make statements nobody in their right mind will believe. And to compound the issue, that is something the leadership doesn’t really seem to take seriously. President Xi Jinping, more than anything else, looks like a man in the tradition of ‘what I say is true because I say so”.
That may have worked for a long time inside the country, but the desire to be part of the global economy means the ‘because I say so’ attitude is now being questioned by people Xi can neither bully nor bend into submission. Something he doesn’t seem to have clued into yet. Surrounded as he will be over these ten days by people who’ll say Yes at any appropriate and inappropriate instance, and laugh at anything he says that might be construed as a joke, Xi won’t come out any the wiser. He’d probably be better off spending those days with someone like Kyle Bass, but he’s not doing that.
Everybody, including most NPC delegates, knows that China’s grossly overleveraged, overproducing and overcapacitated economy needs another round of mass layoffs. Some initial numbers relating to job losses have been ‘leaked’ prior to the Congress. First, it was 1.8 million jobs cut in the coal and steel sectors, and a few days later that became 6 million. But that can only possibly be just a start.
It’s all in the numbers. China has something in the order of a billion workers, give or take 100 million or so. Even with the largest mass migration in human history, in which 100s of millions moved from the countryside to the cities, there are still an estimated 300 million people working in agriculture. That’s the entire US population. It’s also 30% of the Chinese workforce. In the US just 2 or 3% work in farming.
But that still leaves 700 million Chinese in other jobs. Many of these jobs were ‘invented’ in the past 20 years, as China’s ‘miracle growth’ transformed it first into the world’s no. 1 trinket producer, then into a kind of powerhouse that built highways to nowhere cities, and today a powerhouse with a fast plummeting global consumer base.
Many millions of Chinese workers produce things that can’t be sold. This is by no means confined to just coal and steel. The sharply dropping Chinese import and export numbers, as well as the purchasing indices, tell a bleak story. It’s evident that China must re-invent itself. And while that may be exactly what it claims it’s doing, the -alleged- transition to a service- and/or consumer economy may sound good, but its practical success is far from guaranteed.
Transforming a factory worker into a service sector employee is not a matter of flicking a switch. Repeating this 10 million times over, or 20 or 30 million, is a nightmare in an economy that is seeing its growth rates plummet while at the same time needing to deleverage its debt levels.
What are all these people going to do that produces actual economic value? And what will be the character of the companies they produce this value at? China is still dominated by state-owned enterprises, with workers relying on the faith that Beijing will always make everything right that goes wrong.
Losing that faith may have far-reaching consequences. At the same time, China cannot get the international economic status it so desperately seeks if so many de facto work for the government.
Though most tend to forget this, China was in a similar situation not so long ago:
In the late 1990s, China drastically restructured its state-owned enterprises, privatizing some and shutting down others. The result: from 1995 to 2002, over 40 million jobs in the state sector were cut, along with nearly 30 million jobs lost in the manufacturing, mining, and utilities sectors.
Although many of these workers were able to pick up jobs in the newly-growing private sector, the societal and cultural shift entailed in the restricting should not be underestimated. Prior to that wave of reforms, state sector employees (the vast majority of China’s workforce) enjoyed the benefits of an “iron rice bowl,” absolute job security along with social benefits (such as healthcare and pensions) provided by the state.
70 million – unproductive- jobs cut in 7 years. An average 10 million per year. A problem the country ‘solved’ by throwing tens of trillions (in US dollars) into overleveraged overproduction at exports-driven manufacturing enterprises. And by moving hundreds of millions of people into the cities that housed the enterprises.
15 years later, many of these newly created jobs have in their turn become unproductive. And the country may have to start the same process all over again. With probably tens of millions more jobs to replace. Question is, how will it fare this time around? Will people accept it as obediently as 15 years ago?
The reforms of the 1990s resulted in massive lay-offs. Overnight, tens of millions of workers lost their “iron rice bowls.” There were people who didn’t want to accept it, even those who actively resisted, but the government ruled with an iron fist and eventually the reforms went through. Even today, some of these people have grown old on the edge of poverty. On a certain level, we sacrificed them in exchange for huge reforms to the economic system.
But before wondering about civil obedience, let’s ask again: what are all these people going to do that produces actual economic value? Service economy? Consumer economy? There is no move available this time into another giant and overleveraged export industry. They’re at the end of the -debt- line.
Those people that had some money have lost a lot -and will lose much more- in equities and housing markets. Moreover, the government’s attempts to make them feel more secure about their old age would take decades to convince the people. So those who have something to save will do just that. So.. what consumer economy?
Service economy? Much of that in China is in financial services. Which has no future. So what else is there? How about the US model of burger flippers? That looks like a winner…
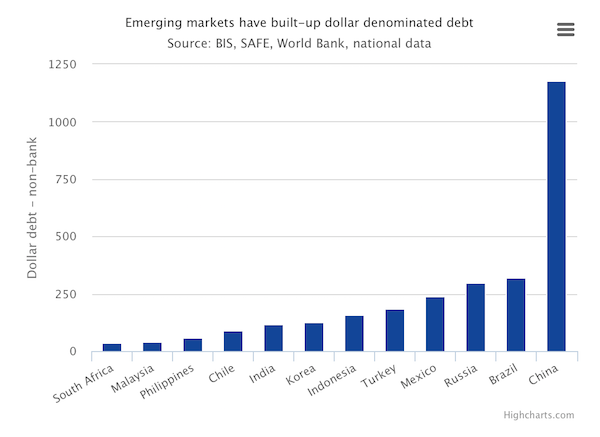
See, here’s a depiction of Chinese debt:
And here’s what they plan to do about it:
It looks like subprime derivatives on steroids: China hopes to bundle together billions of dollars worth of non-performing loans and eventually sell them to global investors Such a massive securitisation programme would represent the latest tactic in China’s campaign to lift one of the biggest shadows cast over its slowing economy -a debt pile that is as big as 230% of GDP. It would whittle back debts at Chinese banks and move some of the risk outside the domestic financial system.
According to official figures, such debts at the banks have reached Rmb1.27tn ($194bn), while analysts estimate the real number is likely to be many times higher. Chinese media has reported that the regulator has granted a total of Rmb50bn for the first wave of products. Demand for the scheme, however, is expected to be significantly more modest than supply. “How many global investors have been interested in the traditional [bad debt in China]?” asked one Hong Kong-based investor with experience buying distressed debt in Asia. “Not many.. is a more complicated version of this going to change that soon? No.”
This’ll be great, as great as the western approach to drowning in debt. Mind you, the Chinese haven’t even started talking about ‘recovery’ like we have, they’re still thinking -or propagandizing- that they’re on an ever upward trail. Well, they’re not. One of the early notes coming out of the People’s Congress was this: “China Says Will Keep Yuan Basically Stable Against Basket Of Currencies ..”
That’s not happening. They know it, we know it, and Kyle Bass knows it. Perhaps once the Congress is over, they’ll come clean? Hard to say. What’s certain is that global markets WILL force a substantial re-adjustment of the yuan, and there’s nothing Xi or the entire Communist Party can do to prevent it. And then, after a 30% readjustment, take another look at that dollar-denominated debt!
And they’ll have to cut many millions of jobs, and try to ‘pacify’ the newly unemployed, and deleverage the insane debt levels they’ve created, and find a way to explain to their people where it all went so wrong.
China no longer lives in a kids’ fantasy Toy Story.